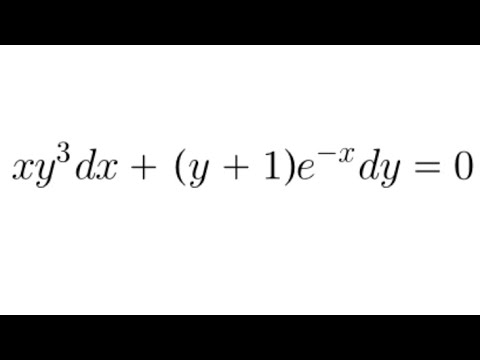
Differential Equations Practice 24 Xy 3dx Y 1 E X Dx 0 Youtube
` (x1)(dy)/(dx) 1 = 2e^(y) , y=0, " when " x=1` A `(x1)(e^(y)2)=2` B `(x1)(e^(y)2)=2` C `xe^(y)2=0` D `(x1)(e^(y)2)=2`Answer (1 of 4) Since the equation is exact on the whole plane, you just integrate with respect to x the coefficient of dx \displaystyle\int(2xe^ye^x)\,dx=x^2e^ye^x\varphi(y) where \varphi is some function Then you differentiate this with respect to y and you have to get the coefficient o
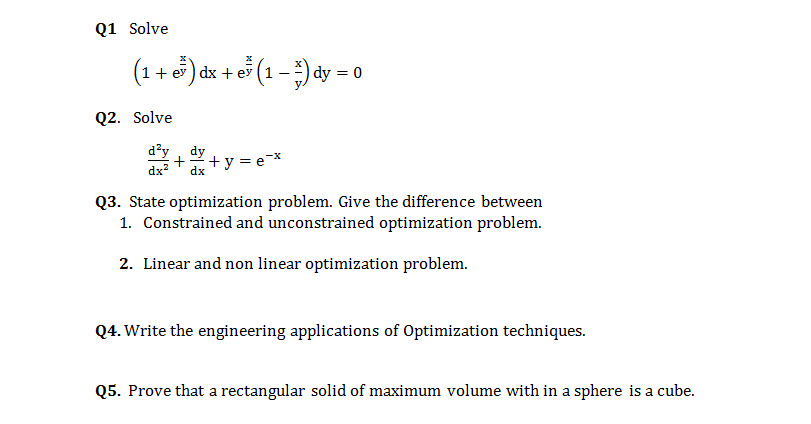
(1 e^x/y)dx e^x/y(1-x/y)dy=0 solution
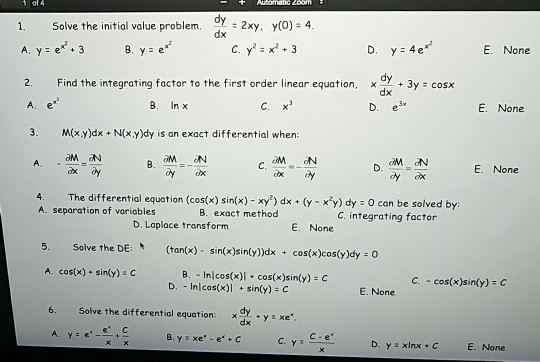
(1 e^x/y)dx e^x/y(1-x/y)dy=0 solution-Ask a Question Solve (1 xy)y dx x(1 – xy)dy = 0 ← Prev Question Next Question → 0 votes 6k views asked in Differential equations by Nakul01 (370k points) Solve (1 xy)y dx x(1 – xy)dy = 0 differential equations;KCET 18 The integrating factor of (dy/dx) y = (1 y/x) is (A) xex (B) xe1/x (ex/x) (D) (x/ex) Check Answer and Solution for above question

Ye X Ydx Xe X Y Y 2 Dy Maths Questions
General form of 1st order and 1st degree differential equation;Solution Verified by Toppr e y(x1)=1 e y×1e y× dxdy ×(x1)=0 Differentiating on both sides ⇒ dxdy = e y×(x1)−e y = x1−1 Differentiating again ⇒ dx 2d 2y = −(x1) 2−1 = (x1) 21 ⇒ dx 2d I'll start with the second one for you Take the natural logarithm of both sides ln(x^y * y^x) = ln(1) ln(x^y) ln(y^x) = 0 yln(x) xln(y) = 0 dy/dxln(x) y/x ln y x/y(dy/dx) = 0 dy/dx(lnx x/y) = lny y/x dy/dx= (lny y/x)/(lnx x/y) dy/dx= (ln y y/x)/(lnx x/y) Now for the second I would differentiate term by term Let t = x^y and u = y^x Then lnt = ln(x^y) and lnu
Thanks for watching like comment and subscribe!Take note we set M as (xy) and N as (xy) in out final answeSolution Verified by Toppr Correct option is D) Given differential equation e y( dxdy −1)=e x y(0)=0 Find y (1)= ?You can write it as a separable equation looking for x(y) instead of y(x) Define first x = log(z) which leads to y2z′ −yz z2 = 0 Now, define z = u1 which leads to
(1 e^x/y)dx e^x/y(1-x/y)dy=0 solutionのギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 |  | |
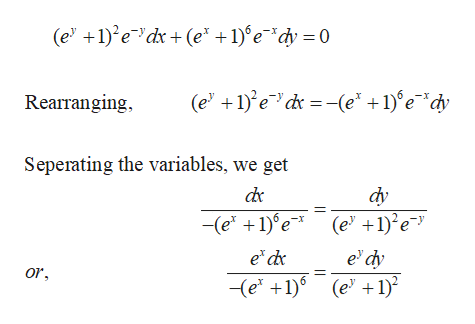 | 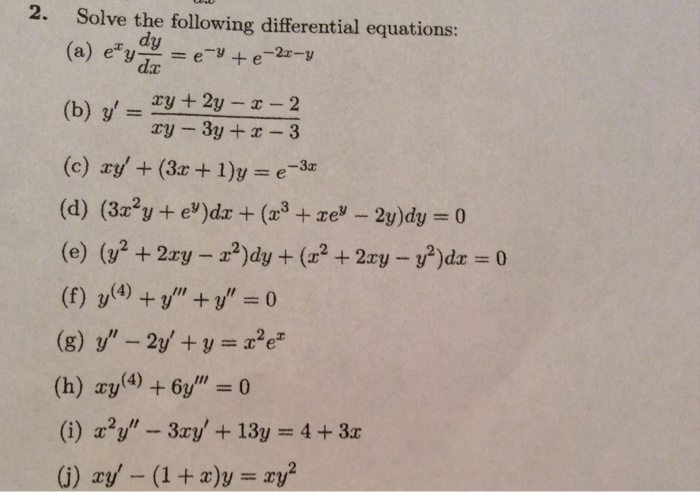 | 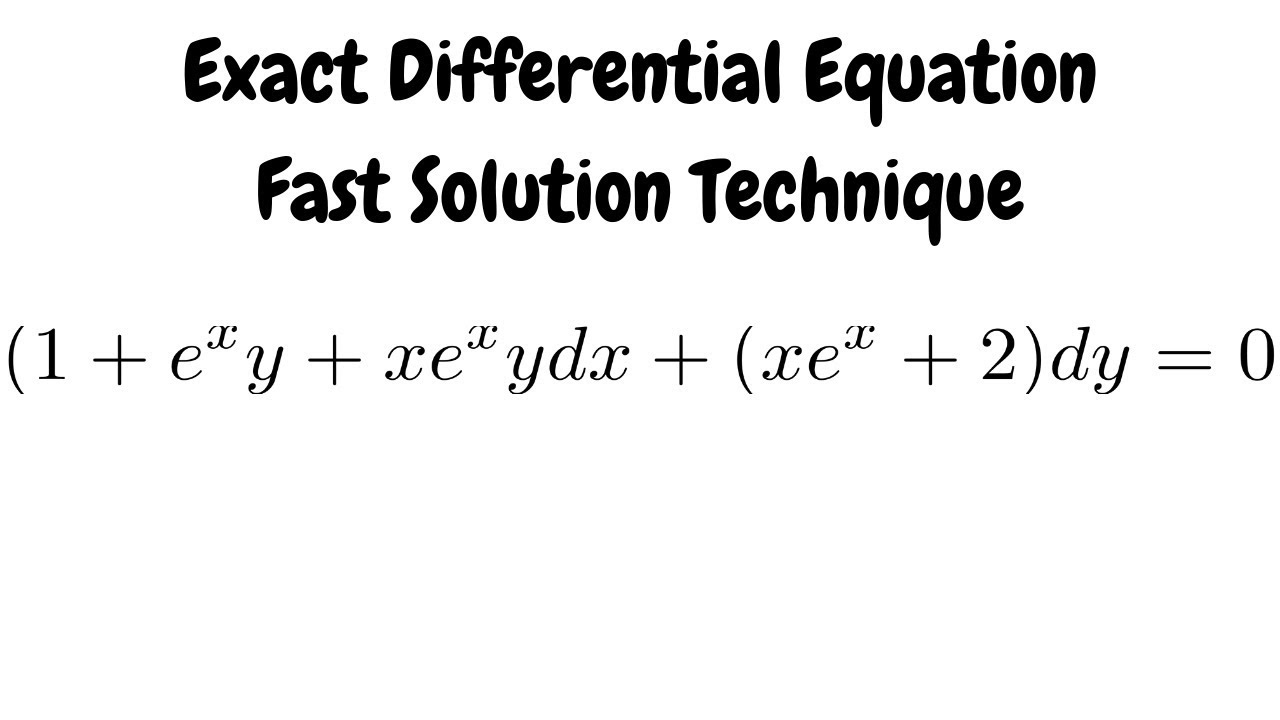 |
 |  |  |
「(1 e^x/y)dx e^x/y(1-x/y)dy=0 solution」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「(1 e^x/y)dx e^x/y(1-x/y)dy=0 solution」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 | 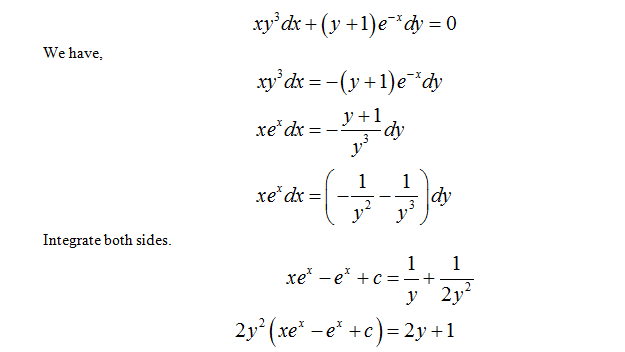 |  |
「(1 e^x/y)dx e^x/y(1-x/y)dy=0 solution」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 | ||
 |  | |
「(1 e^x/y)dx e^x/y(1-x/y)dy=0 solution」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | 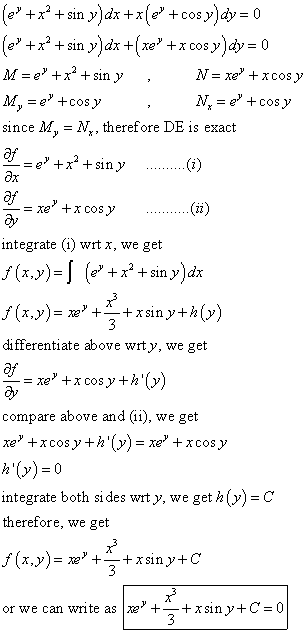 |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「(1 e^x/y)dx e^x/y(1-x/y)dy=0 solution」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  | |
「(1 e^x/y)dx e^x/y(1-x/y)dy=0 solution」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「(1 e^x/y)dx e^x/y(1-x/y)dy=0 solution」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「(1 e^x/y)dx e^x/y(1-x/y)dy=0 solution」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 | 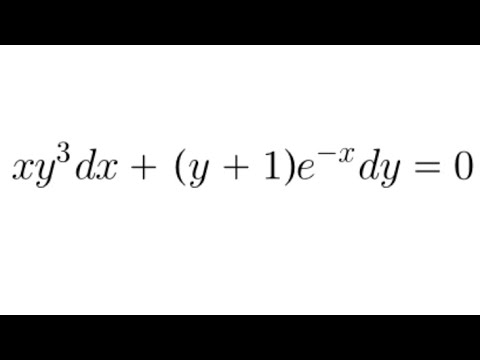 | 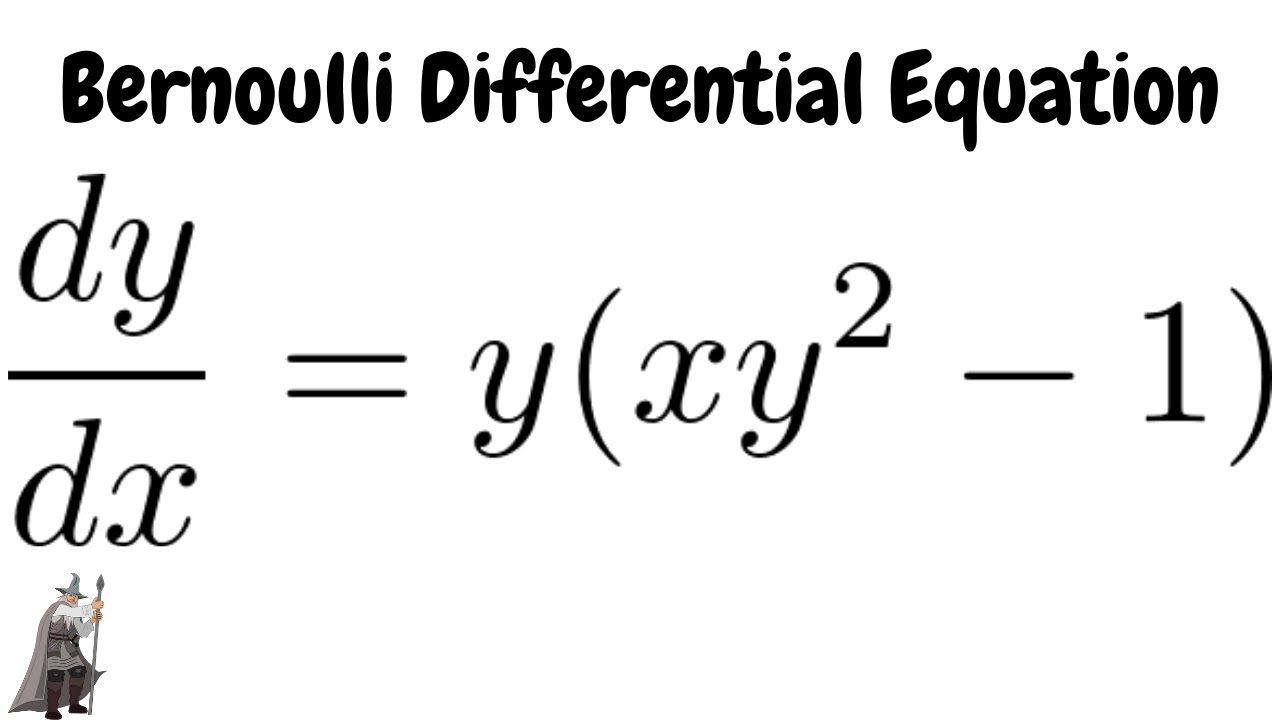 |
 |  |  |
「(1 e^x/y)dx e^x/y(1-x/y)dy=0 solution」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
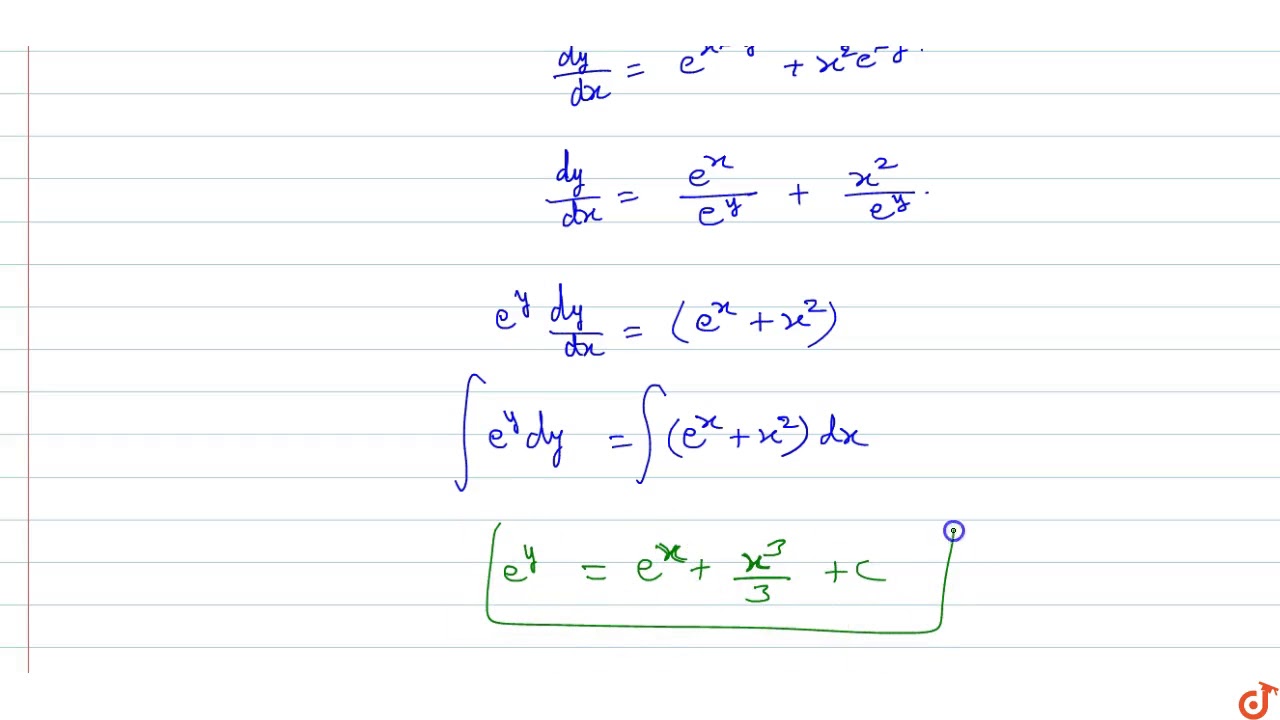 |  |  |
「(1 e^x/y)dx e^x/y(1-x/y)dy=0 solution」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「(1 e^x/y)dx e^x/y(1-x/y)dy=0 solution」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |
y = cos^1(e^(cx)) Given e^x(cos(y)dxsin(y)dy)=0 Distribute e^x across the terms e^xcos(y)dxe^xsin(y)dy=0 This is of the form M(x,y)dx N(x,y)dy = 0 where M(x,y) = e^xcos(y) and N(x,y) = e^xsin(y) Check for exactness (delM(x,y))/(dely) = e^xsin(y) (delN(x,y))/(delx) = e^xsin(y) The equation is exact, therefore, there exists a solution, F(x,y), such that F(x,y) = CSimple and best practice solution for Y(1x)DXx(1y)dy=0 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve it





0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿